Applications and Benefits of Lithium batteries: Li-SOCL2 battery, lithium polymer battery, ultra-thin battery, LiMnO2 battery and high-temperature batteries
Applications and Benefits of Lithium batteries: Li-SOCL2 battery, lithium polymer battery, ultra-thin battery, LiMnO2 battery and high-temperature batteries
In the rapidly evolving world of battery technology, lithium batteries have established themselves as a leading choice for a wide range of applications, owing to their high energy density, low self-discharge rate, and long shelf life. Among the various types of lithium batteries, Li-SOCL2, lithium polymer, ultra-thin, lipo, Lithium Manganese Dioxide (LiMnO2), and high-temperature batteries stand out as pioneers in their respective fields. This article delves into the advancements, characteristics, and applications of these batteries, focusing on their unique selling points and the benefits they offer to end users.
1. Lithium-SOCL2 (Lithium Thionyl Chloride) Battery
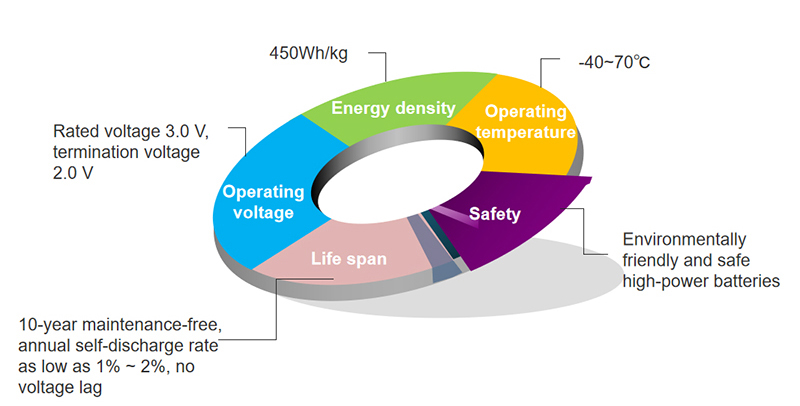
Lithium-SOCL2 batteries, also known as Li-SOCL2 or Lithium Thionyl Chloride batteries, are a type of primary (non-rechargeable) battery that offers exceptional energy density and stability. These batteries operate at a nominal voltage of 3.6V and are known for their high energy capacity and ultra-long shelf life. The Li-SOCL2 chemistry allows for a low self-discharge rate, ensuring that the battery retains its charge for extended periods, even when not in use.
One of the leading manufacturers of Li-SOCL2 batteries has capitalized on these unique properties to cater to applications that require long-term, reliable power. These batteries are ideal for use in mission-critical devices such as spacecraft, satellites, and military systems. Their ability to provide consistent power over extended periods, with minimal maintenance, makes them a valuable asset in remote and inaccessible locations.
Lithium sulfuryl chloride (Li-SOCl2) batteries are renowned for their long shelf life and high energy density. They are commonly used in applications where long-term, reliable power is crucial, such as in military and aerospace equipment. Their stability at high temperatures makes them suitable for extreme environments.
2. Lithium Polymer Battery
Lithium polymer batteries, commonly referred to as LiPo or LIP batteries, represent a significant advancement in rechargeable battery technology. These batteries use a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid electrolyte, resulting in a lighter, more flexible design. Lithium polymer batteries are known for their high energy density, fast charging capabilities, and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
The flexibility of lithium polymer batteries allows for innovative designs and shapes, making them a popular choice for consumer electronics, such as smartphones and tablets. Additionally, their high energy density and fast charging capabilities are crucial for applications that require rapid power delivery, such as electric vehicles and drones. The leading manufacturers of lithium polymer batteries continue to push the boundaries of battery performance, aiming to deliver even higher energy densities and improved safety.
Lithium polymer batteries, also known as lithium-ion polymer batteries, offer a combination of high energy density and flexibility. Their lightweight and thin design allow them to be integrated into various devices, from smartphones to wearable technology. Lithium polymer batteries are also safer than traditional lithium-ion batteries, reducing the risk of fire or explosion.
3. Ultra-Thin Batteries
Ultra-thin batteries are designed to meet the demand for increasingly compact and lightweight devices. These batteries feature an ultra-slim profile, often less than 1mm thick, while maintaining sufficient energy density to power the device. Ultra-thin batteries are commonly used in wearable electronics, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, where space is limited but power requirements are still significant.
Leading manufacturers of ultra-thin batteries have achieved significant breakthroughs in battery technology, resulting in batteries that are thinner and lighter than ever before. These advancements have enabled the development of innovative wearable devices that offer unprecedented functionality and convenience to users.
Ultra-thin lithium batteries are an ideal solution for devices that require minimal thickness. They are commonly used in smart cards, RFID tags, and other miniaturized electronics. The thin profile of these batteries enables them to fit into spaces that were previously inaccessible, opening up new possibilities for device design.
4. Lithium Manganese Dioxide Battery (LiMnO2)
Lithium Manganese Dioxide (LiMnO2) batteries are a type of primary battery that offers high energy density and a stable discharge voltage. These batteries operate at a nominal voltage of 3V and are commonly used in applications that require reliable, long-lasting power. LiMnO2 batteries are known for their excellent shelf life and low self-discharge rate, making them ideal for use in devices that need to be stored for extended periods before use.
Leading manufacturers of LiMnO2 batteries have optimized the chemistry and design of these batteries to achieve even higher energy densities and improved performance. These advancements have enabled the use of LiMnO2 batteries in a wider range of applications, including medical devices, security systems, and remote sensors.
Lithium manganese dioxide (LiMnO2) batteries are known for their stable performance and cost-effectiveness. They are widely used in consumer electronics, such as hearing aids and digital cameras, due to their ability to provide consistent power over long periods. LiMnO2 batteries are also environmentally friendly, making them a sustainable choice for energy storage.
5. High-Temperature Battery
High-temperature batteries are designed to operate reliably in extreme temperature conditions, often exceeding 100°C. These batteries are essential for applications in harsh environments, such as aerospace, automotive, and industrial sectors. High-temperature batteries must be able to withstand the thermal stress and maintain stable performance, even under extreme operating conditions.
Leading manufacturers of high-temperature batteries have developed innovative battery chemistries and designs to ensure reliable operation in high-temperature environments. These batteries are tested rigorously to ensure that they can meet the demanding requirements of their target applications. As a result, high-temperature batteries play a crucial role in ensuring the reliable operation of critical systems in extreme environments.
High-temperature lithium batteries are designed to operate at elevated temperatures, often exceeding 100°C. They are crucial in applications where conventional batteries would fail, such as in downhole oil and gas exploration. High-temperature lithium batteries can maintain their performance even in extreme heat, ensuring reliable power supply in harsh environments.
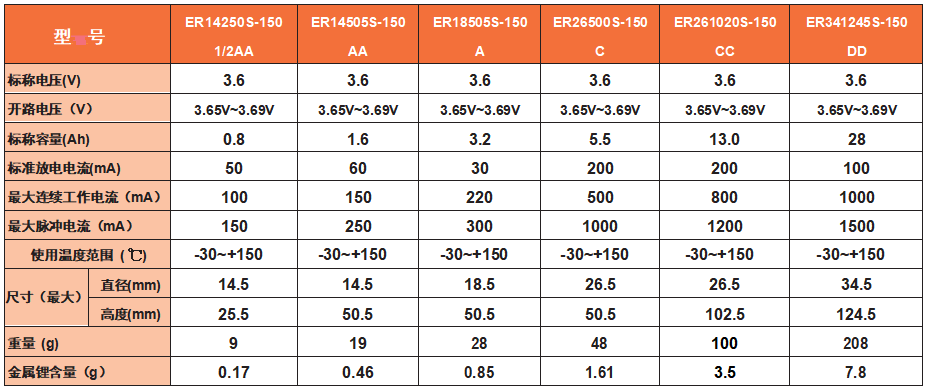
In conclusion, lithium batteries offer a versatile solution for energy storage, with different types suiting a wide range of applications. From Li-SOCl2 batteries for military and aerospace use to ultra-thin lithium batteries for miniaturized electronics, lithium batteries continue to evolve and innovate, providing more efficient and reliable power sources for our modern world. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more applications and benefits of lithium batteries in the future.





